How Audiences Are Reshaping Mass Media: Marketing, Culture, and Technology in the AI Era
Video created by Nevada Gray Studio using Google Veo3
Why Public Behavior Now Drives the Future of Mass Media
Mass media influence has changed from a top-down broadcast model to a bottom-up, audience-driven ecosystem shaped by participation, technology, and cultural expectation. Algorithmic platforms, AI-generated influencers, creator economies, and live shopping increasingly reflect how people interact, socialize, and make meaning in real time. Industry research from Deloitte’s Digital Media Trends (2025) shows that social platforms now operate as blended entertainment, commerce, and community spaces, while Pew Research Center (2025) documents declining trust in institutional media alongside growing reliance on creators and peer networks for credibility and connection. Peer-reviewed studies further reinforce this transformation, finding that live shopping and IRL (in real life)-style interactions increase trust, community, emotional engagement, and perceived authenticity by replicating social culture at scale (Hou & Hou, 2024; Wang et al., 2022). Together, these dynamics explain the parallel rise of AI influencers, livestream commerce, and experiential brand formats that prioritize immediacy, entertainment, and relational connection over static one sided messaging (Zu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024).
CNBC. (2025, March 30). How TikTok Shop became the fastest growing social media shopping platform [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XLFhfwVOPaI
From a marketing perspective, this signals a seismic shift. Audiences increasingly determine what succeeds in mass media by rewarding formats that feel inclusive, emotionally intelligent, and responsive to lived experience. Traditional campaign logic optimized for reach and frequency delivers diminishing returns in environments where attention flows toward interaction, co-creation, and shared moments. Brands that recognize this inversion of influence gain strategic advantage by aligning media strategy with how culture now forms rather than how it once circulated (Myers, 2025). TikTok Shop accounted for 20% of U.S. social commerce in 2025 and is projected to exceed $20 billion in sales by 2026, with 50% of U.S. social shoppers projected to purchase on the platform. Live shopping trends illustrate how creator-led content now drives mass media behavior, requiring brands to develop content and messaging systems capable of scaling emotional relevance and cultural resonance across six living generations simultaneously (Walk-Morris, 2025).
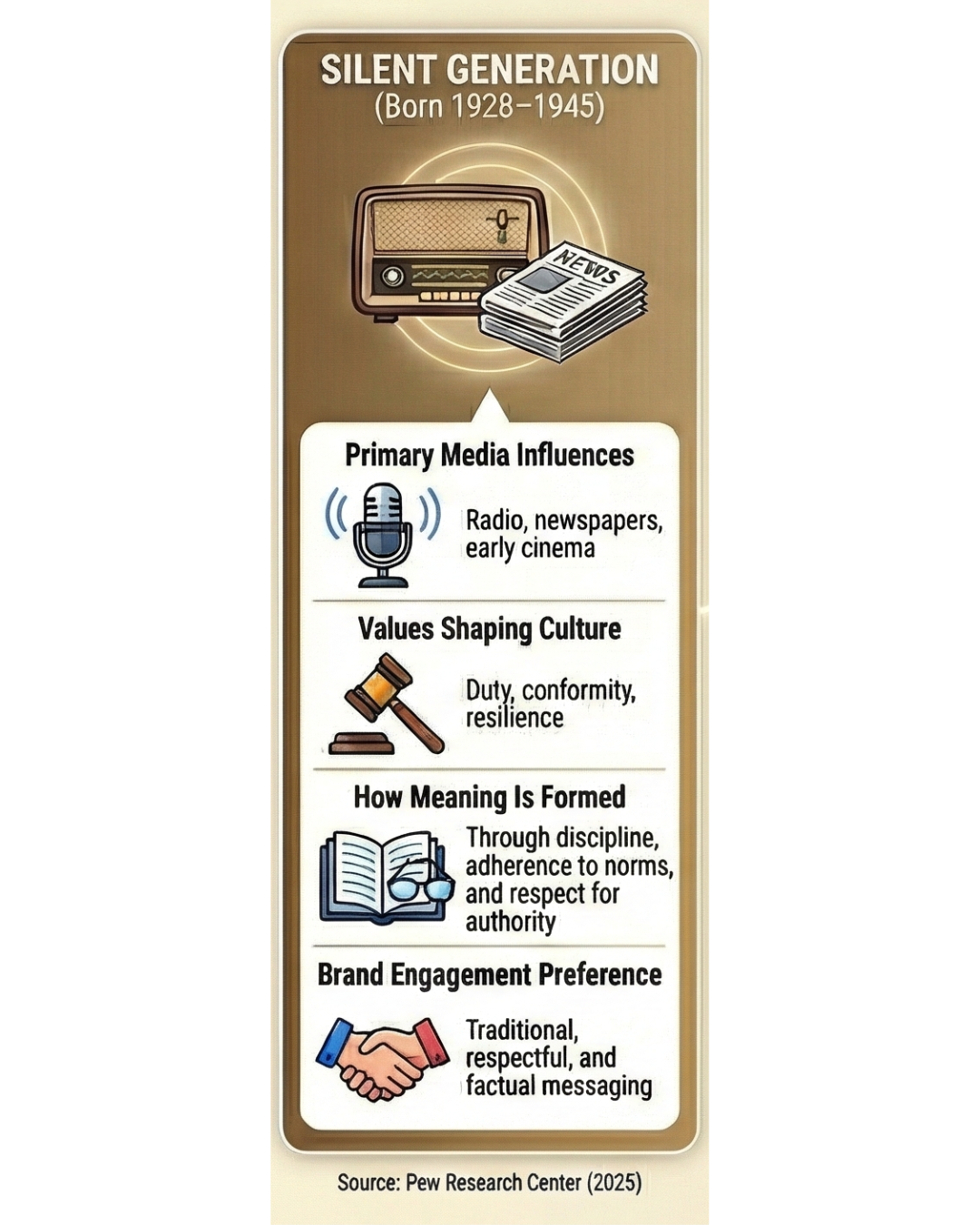
The Silent Generation’s media habits and cultural values were shaped by early mass communication systems, illustrating the foundational trust structures that continue to influence how more mature audiences engage with brand messaging in modern media (Baran, 2024). Graphic created by Nevada Gray Studio.
Generational Media Expectations in 2026 and What They Mean for Brand Messaging
Values shaping culture by generation. Graphic created by Nevada Gray Studio.
Technology has fragmented mass media into generation-specific value systems, making universal messaging increasingly ineffective. In 2025, Generation Alpha (born 2010–present) emerged as the first fully AI-native generation, influenced by immersive gaming, voice interfaces, visual-first learning, and parent-mediated digital ecosystems that emphasize interactivity and psychological safety. Generation Z (born 1997–2009) values authenticity, creator transparency, and participatory culture informed by algorithmic discovery platforms such as TikTok. Millennials (born 1981–1996) prioritize emotional intelligence, community belonging, and values alignment shaped by economic volatility, wellness culture, and digital fatigue. Generation X (born 1965–1980) emphasizes efficiency, credibility, and practical utility, while Baby Boomers (born 1946–1964) remain more influenced by institutional trust cues and legacy media norms (Baran, 2024). The one human value that connects all six living generations is belonging, expressed through the shared need to feel acknowledged, included, and connected across evolving cultural and technological contexts.
The Evolution of Marketing. Video created by Nevada Gray Studio using Google Veo3
For brands, these differences highlight an opportunity to move past one-size-fits-all marketing toward responsive storytelling systems that adapt across AI influencers, IRL experiences, live shopping, and community-led entertainment. Research on social commerce demonstrates that audiences respond more positively when brands create community, interactive, and emotionally resonant content versus promotional (Baran, 2024). The cultural blind spot facing modern marketing is not a lack of technology, but an overreliance on persuasion-driven models in an era where audiences increasingly seek co-creation, entertainment, and shared purpose. Content strategies that flex across generational values while maintaining transparency and ethical consistency are better positioned to resonate with consumers.
Cultural Effects and Improvement Plan: Aligning Media Systems With How Culture Forms
As AI-based algorithmic systems continue to mold cultural participation, marketers will benefit from evolving toward approaches that balance performance with generational connection. Studies on live commerce and social presence suggest that real-time interaction, visible human involvement, and experiential design strengthen trust and perceived authenticity in digital environments (Hou & Hou, 2024). Brands may find value in transitioning from campaign-centric execution toward adaptable storytelling frameworks that operate across AI influencers, IRL activations, livestream commerce, and community-driven entertainment, while maintaining consistent transparency and ethical standards (Gottfried & Park, 2025; Widener et al., 2025). Incorporating human moderation, clarity, and interactive content supports a media ecosystem where algorithmic efficiency and cultural cohesion reinforce one another. This approach reflects a broader cultural recalibration in which mass media succeeds not by directing audiences, but by designing experiences that invite co-creation and community.
References:
Baran, S. J. (2024). Media and culture in the digital age. In Introduction to mass communication: Media literacy and culture (13th ed., pp. 305–333). McGraw Hill
Eddy, K., & Shearer, E. (2025, October 29). How Americans’ trust in information from news organizations and social media sites has changed over time. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2025/10/29/how-americans-trust-in-information-from-news-organizations-and-social-media-sites-has-changed-over-time/
Gottfried, J., & Park, E. (2025, November 20). Americans’ social media use 2025. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2025/11/20/americans-social-media-use-2025/
Hou, K., & Hou, T. (2024). Understanding trust and attachment transfer in the context of live streaming: An empirical investigation. Current Psychology, 43, 17239–17253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-05685-3
Myers, J. (2025). Participatory media theory. In Media ecology for the 21st century. Palgrave Macmillan. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-04032-9_9
Walk-Morris, T. (2025, December 18). TikTok Shop is driving social commerce growth. Retail Dive. https://www.retaildive.com/news/tiktok-shop-drives-social-commerce-growth/807665/
Wang, Y., Lu, Z., Cao, P., et al. (2022). How live streaming changes shopping decisions in e-commerce: A study of live streaming commerce. Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW), 31, 701–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10606-022-09439-2
Widener, C., Arbanas, J., Van Dyke, D., Arkenberg, C., Matheson, B., & Auxier, B. (2025). 2025 digital media trends: Social platforms are becoming a dominant force in media and entertainment. Deloitte Insights. https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/technology/digital-media-trends-consumption-habits-survey/2025.html
Xu, B., Dastane, O., Aw, E. C.-X., & Jha, S. (2025). The future of live-streaming commerce: Understanding the role of AI-powered virtual streamers. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 37(5), 1175–1196. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-03-2024-0263
Zhang, X., Shi, Y., Li, T., et al. (2024). How do virtual AI streamers influence viewers’ livestream shopping behavior? The effects of persuasive factors and the mediating role of arousal. Information Systems Frontiers, 26, 1803–1834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-023-10425-2
Nevada Gray Studio.